
Today we’re going to talk about a quite particular distro: Void Linux. It´s a distribution built from scratch, which means that it is not based on any of the principal distros that we know.
The main features are:
- Kernel 5.4.49 LTS.
- Rolling release.
- Runit init system, a replacement for sysvinit, systemd-free, which is really faster.
- His own package management, called XBPS, built from scratch.
For those that work with Linux since a while, and probed many distros, we will notice certain similarities between Void Linux and other distributions like Arch or Slackware. We can say that Void Linux uses KISS (Keep It Simple Stupid) philosophy.
Void Linux is available for a lot of architectures like x86, x86_64, Raspberry, Odroid, and many more. They also offers different installation images, from network / CLI install to live images with differents flavors like Xfce, Cinnamon, Enlightenment, Mate, LXDE and LXQT.
Void Linux Installation Guide
Configuration and installation is really simple. We have a CLI Installer, it’s the same in all of the available images, and we call him with the “void-installer” command (using sudo).
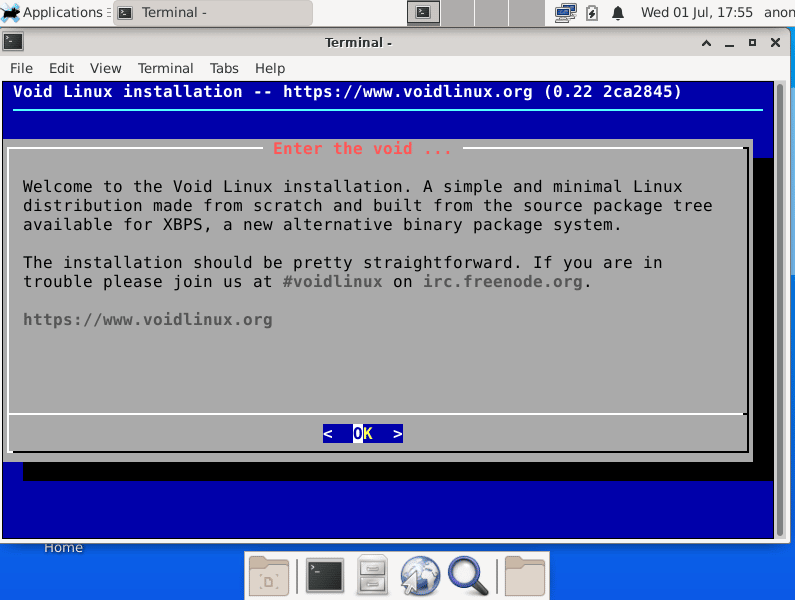
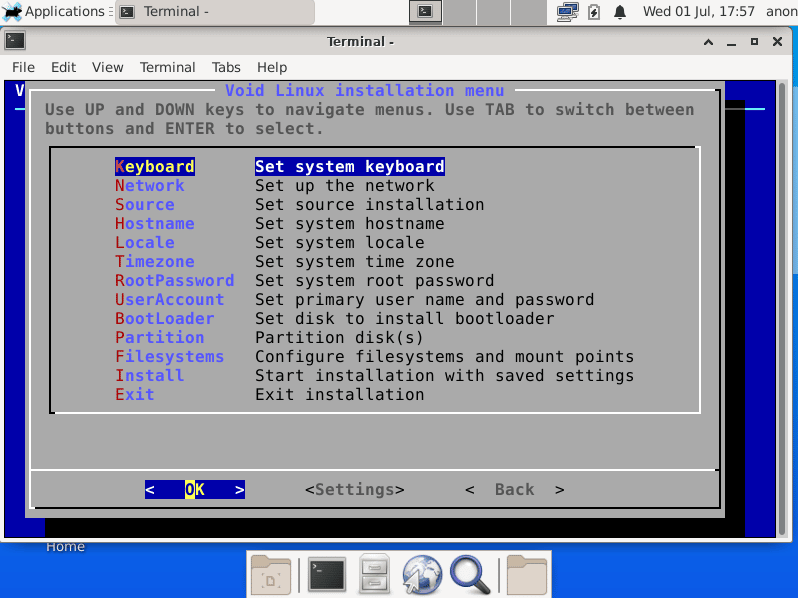
It has the common options like other CLI installers, but I will explain the following:
Source
Here we can choose between two options: Local o Network . Local will install the contents of the live image, in this example, the contents of the XFCE live image. Network will make a base installation from their repositories, but once installation is finished, we will need to install and configure the desktop environment.
In case you choose local installation, you’ll need to make an update after system install.
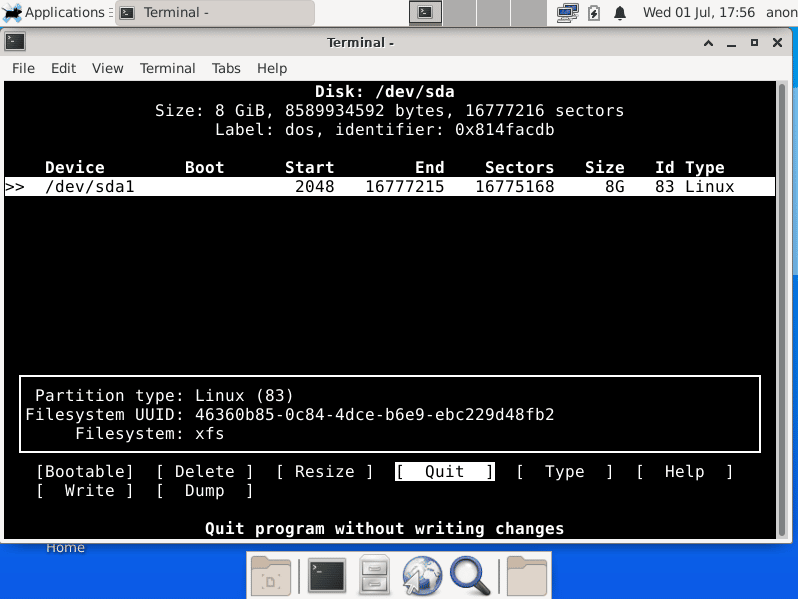
Partition
Here you’ll create partitions with cfdisk to install the OS. At least, I recommend to create a 10GB partition. Once this is made, you need to write changes to the disk and return to the installer menu to continue with Filesystems option.
Filesystems
Here you’ll format the created partitions with the filesystem of your preference and assign the mountpoint.
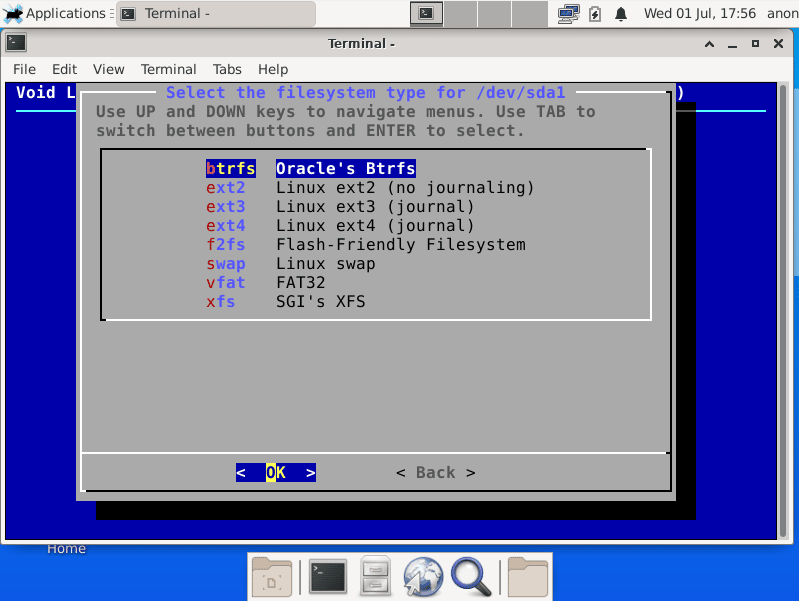
Once you’ve done with all the misc configurations, the Install option will write the changes to the disk. After that, you will be asked to reboot the system, or you can continue testing from the live session.
Void Linux Troublesh
Known for its simplicity and being a rolling release distro, Void Linux uses the xbps package manager and offers options with various desktop environments. If you’re encountering issues with Void Linux, here’s a generalized troubleshooting guide:
1. Package Management Issues with XBPS:
- Update Your System: Always ensure your system is up-to-date.
sudo xbps-install -Su- Search for Packages: If you’re not sure about the name of a package:
xbps-query -Rs [search-term]- Fix Broken Installations:
sudo xbps-install -f2. Boot Issues:
- If the system doesn’t boot, check the GRUB bootloader settings. You might need a live USB of Void Linux or any other Linux distribution to repair it.
- Ensure the kernel and initramfs entries in the GRUB configuration point to the correct locations.
3. Networking:
- Use
ip ato check your network interfaces. If an interface likeeth0orwlp3s0(names might vary) doesn’t have an IP address, you might need to restart your network services. - If using DHCP, ensure the
dhcpcdservice is enabled and running.
4. Desktop Environment Issues:
- If your desktop environment doesn’t start correctly, try starting it manually from a terminal using the command associated with that environment, like
startxfor some setups. - Check for error messages in the
~/.xsession-errorsfile.
5. Logging and Monitoring:
- Use
dmesgorjournalctlto check system logs, which can provide hints about any hardware or software issues.
6. Dependencies and Libraries:
- If a specific program doesn’t run, it might be missing libraries. Use:
ldd /path/to/programThis will show the shared libraries required and if they’re found.
7. User and Permissions Issues:
- If a service doesn’t start or an application fails to run, check if it has the necessary permissions. Some applications need to be run with
sudoor as the root user.
8. Check Void Linux Forums and Documentation:
- The Void Linux forums and official documentation are excellent resources. Someone may have already encountered and solved the same issue.
Final Thoughts
Void Linux is an attractive option for those who loves KISS philosophy. XBPS it’s an easy and robust package manager and, by the way, runit it’s really awesome, fast and a very interesting option for those who hate systemd.
Troubleshooting in Void Linux, like other distributions, often requires a methodical approach. Identifying symptoms, understanding system logs, and consulting the distro’s community can all aid in resolving issues.
Also read: Void Linux in Spanish version
2 thoughts on “Void Linux at a glance”